Solar cell: a device that generates an electric current from sunlight.
biomass conversion: getting energy from plant and animal materials by changing them into high-quality fuels.
nuclear fission: the splitting of nucleus with a large mass into two nuclei with smaller masses.
chain reaction: a reaction that is kept going by products of the reaction.
nuclear fusion: the merging of nuclei with smaller masses into a nucleos with a larger mass.
hydroelectricity: the use of flowing water to generate electricity.
thermal pollution: the excess heating of the enviroment.
Thermal expansion: the expansion of matter when its temperature is raised.
pressure: the force on each unit of area of a surface.
melting: the change of a solid into liquid.
vaporization: the change ofliquid to gas as molecules break free from each other.
Condensation: the change of gas into a liquid as molecules attract each other.
freezing: the change of a liquid into a solid.
boiling: the formationof bubbles of vapor that escape from a liquid that is being heated.
evaporation: the vaporization of molecules from the surface of a liquid.
Kinetic energy: the energy of a moving object.
Pottential energy: energy stored in an object or material.
Temperature: the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a material.
Heat: energy that flows between pbjects that have different temperatures.
Radiation: the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves.
Conduction: the transfer of energy byeby direct contact of molecules.
Convection: the transfer of energyby the flow of aa liquid or gas.
Insulation: prevents heat from flowingin or out of a material.
Compound: a chemical combination of two or more elements.
Chemical bond: a link that atoms or electrically charged particles can form with each other.
Chemical formula: a way of using letters and numbers to show how much of each element is in a substance.
Ion: an electrically charged particle with unequal numbers of prtons and electrons.
Molecule: a group of bonded atoms that acts like a single patricle.
Chemical property: a way of describing how a substance changes chemically with other substances.
Exothermic: a reaction that give off heat.
Endothermic: a reaction that absorbs heat.
Element: a substance that cannot be broken down any further into anything simpler.
Atom: the smallest particle of an element that has the same chemical properties as the elements.
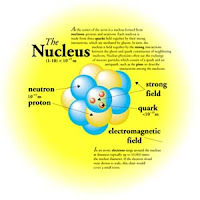
Nucleus: an atom`s dense center, where most of it mass is.
Electron: a negatively charged particle that moves around an atom`s nucleos.
Proton: a positively charged particle inside an atom`s nucleus.
Neutron: a particle with no charge inside an atom`s nucleos.
Atomic Number: the number of protons in an atom.
Metal. any of a group of elements that conduct heat and electricity, is shiny and bendable.
1. Matter: any solid, liquid or gas.
2. Mass: amount of matter in an object.
3. volume: the amount of space an object takes up.
4. Density: the amount of mass in a certain volume of material.
5. Physical Property: a property that can be observed without changing the the identidy of a substance.
6. Physical Change: a change in size, shape, or state without forming a new substance.
7. Solution: a mixture of one substance dissolved in another so that the properties are the same throughout.
8. Chemical change: a change in matter that produce a new substance withh different properties of the original.
Abandoned Farm- First year a comunity of crabgrass, insects and mice,
invades the field were corn once grew.
Second and third years ragweed, and tall grasses grow among the crabgrass. It can easily survive in the shade cast.
Four to Six Year Later The hot, dry field of tall weeds provides a perfect environment. More birds join the community.
Twenty five years later pine forest has replaced the old farm field. Yet the number of new pine seedlings drops bacause they can´t grow in the shade.raccoons and foxes begin to visit.
One Hundred Years Later The forest is now mostly decidius trees. These trees are habitats of many different kind of animals.