Abandoned Farm- First year a comunity of crabgrass, insects and mice,
invades the field were corn once grew.
Second and third years ragweed, and tall grasses grow among the crabgrass. It can easily survive in the shade cast.
Four to Six Year Later The hot, dry field of tall weeds provides a perfect environment. More birds join the community.
Twenty five years later pine forest has replaced the old farm field. Yet the number of new pine seedlings drops bacause they can´t grow in the shade.raccoons and foxes begin to visit.
One Hundred Years Later The forest is now mostly decidius trees. These trees are habitats of many different kind of animals.
sábado, 27 de noviembre de 2010
jueves, 18 de noviembre de 2010
Summary#6 Places to live around the world
There are two biomes: Land and water biome, the water biome is divided in 2: fresh water and salty water. The fresh water is divided in 3: the plankton that floot in the water, Nekton that swim through the water, Benthos: bottom-dwelling. Salty water is divided in 2 : interdial: 200m depth, Open ocean is upper region 100-200 depth - Lower region: 200-1000m depth.
The land biome is divided in 6: Desert, Tundra, Grassland, Decidious Forest, Taiga, Tropical Rain Forest.
Salty Water
The land biome is divided in 6: Desert, Tundra, Grassland, Decidious Forest, Taiga, Tropical Rain Forest.
Salty Water
Fresh water
martes, 26 de octubre de 2010
Summary #5 Surviving in the Ecosystem
Animals are important because they control the population. Like, with frogs there were many insect or if there is no lions there were many deers.There are many animals that adapt like the polar bear in cold places. He adapts with his skin, his claws, the clouds and many others. If he will be in Panama he will die. That is the same with the camel if he will go to antartida he will die. But the only animal that an be adapted in all places is the human. The human doesn't have skin or fingernails that is use to be adapted but we have one thing intelligence.Now were going to talk about symbiosis. Symbiosis is oraganism relating for a long time.Symbiosis is divded in three. Parasitism, Mutualism and commensalism. Parasitisim is One organism benefits and the other harms.One example is the flea nad the dog. The flea benefits and the dog harms. Another example is the plant and coling dobber plant. The coiling dobber plant benefits and the plant harms. Mutalism is Both oraganism benefits.One example is the yucca tree and the yucca months. The yucca month help the yucca tree to reproduce.Commensalism is one organism benefits and the other does not harms. One example is the orchid and the trees.
Summary # 4 - Cycles of Life
There are many cycle. But the more importants are water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. The water cycle begins with evaporation. Next with condesation that includes precipitation also . Then the freezing. Finally the evaporation again. The carbon cycle includes the living things and some gases. The persons , fire and cars give to the plants CO2 and the plants need it to grow. And the plants give us HO2 for survive. Finally we hhave the nitrogen cycle. It begins with the atmosphere . Then it goes to the soil that creates the ammonia the the nitrites and finally the nitrates. After we start over. The nitrogen is the more necesary of the gases.
lunes, 18 de octubre de 2010
summary #3 - Food chain and Food web
Food chain is energy and Food web is eating.In Food chain start with the sun then with a leaf . After with a worm. Next with a chicken. Then with the human. And finally with a bacteria. The more powerful of all. Now the food Web. We have a tree ( producer) , a Jiraffe( consumer 2 class Herbivorous) , a Leon ( cosumer 1 class carnivorous) and a bacteria ( consumer diposed) The leon eats the jiraffe the jiraffe eats the tree( leaves) and the bacteria eats the jiraffe and the lion.
Summary #2 - animals and their enviroment
The ecosystem are divided in two that are biotic and abiotic. Biotic are living things and abotic are non-living things. The biotics are divided the protist, the animals , plants , fungi and bacteria. The abotics are divided in minerals, rocks , air , light , soil ,and water . The virus are not considered biotics because they have to be in other organism to be alive.
sábado, 16 de octubre de 2010
Summary #1 Energy Resources
Energy resources is about ways of getting energy so we can generate electrical power.
Solar power. that's obvious, but the energy in coal originally came from the sun too.Prehistoric plants stored the sun's energy in their leaves, and when they died they eventually formed coals seams, the energy was still there.So when we burn coal (or any fossil fuel), we're releasing chemical energy that was stored in plants millions of years ago.
The same goes for wind and wave power.Waves occur because of winds, and winds blow because the sun warms our atmosphere.Warm airs tends to rise, and winds are due to other air moving in to replace it.
Most power stations burn coal, oil or natural gas to run the generators.Others use uranium, or the flow of water. Electricity is sent around the country using high-voltage power lines. Nearly all of the power we use comes from large power sations, altough some places such as isolated farms, or hospitals, have their own diesel generators.
Solar power. that's obvious, but the energy in coal originally came from the sun too.Prehistoric plants stored the sun's energy in their leaves, and when they died they eventually formed coals seams, the energy was still there.So when we burn coal (or any fossil fuel), we're releasing chemical energy that was stored in plants millions of years ago.
The same goes for wind and wave power.Waves occur because of winds, and winds blow because the sun warms our atmosphere.Warm airs tends to rise, and winds are due to other air moving in to replace it.
Most power stations burn coal, oil or natural gas to run the generators.Others use uranium, or the flow of water. Electricity is sent around the country using high-voltage power lines. Nearly all of the power we use comes from large power sations, altough some places such as isolated farms, or hospitals, have their own diesel generators.
martes, 28 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary 16- Earth's Water Supply
desallination: getting fresh water fro seawater.
water cycle: the continious movement of water between Earth's surface and the air, hanging from liquid to gas to liquid.
groundwater: water that seeps into the ground into spaces between bits of rock and soil
water table: the top of the water-filled spaces in the ground.
aquifer: an underground of rock or soil filled with water.
spring: a place were groundwater seeps out of the ground.
well: a hole dug below the water table that water seeps into.
reservoir: a storage area for freshwater supplies.
water cycle: the continious movement of water between Earth's surface and the air, hanging from liquid to gas to liquid.
groundwater: water that seeps into the ground into spaces between bits of rock and soil
water table: the top of the water-filled spaces in the ground.
aquifer: an underground of rock or soil filled with water.
spring: a place were groundwater seeps out of the ground.
well: a hole dug below the water table that water seeps into.
reservoir: a storage area for freshwater supplies.
Vocabulary 15- Earth's Atmosphere
renewable resource: a resource that can be replaced in a short period of time.
ozone layer: a layer of ozone gas in the atmosphere that screens out much of the sun's UV rays.
fossil fuel: a fuel formed from a decay of ancient forms of life.
smog: a mixture of smoke and fog.
acid rain: moisture that falls to Earth after being mixed with wastes fro burned fossil fuels.
ozone layer: a layer of ozone gas in the atmosphere that screens out much of the sun's UV rays.
acid rain: moisture that falls to Earth after being mixed with wastes fro burned fossil fuels.
vocabulary 14 - Earth's Rocks an Soil
rock: a naturally solid in the crust, made up of one ore more minerals.
igneous rock: a rock formed when melted rock materials cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock: a rock made of bits of matter joined together.
fossil: any remanins or printing of living things of the past.
methamorphic rock: a rock formed under heat and pressurefrom another kind of rock.
humus: decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution: adding any harmfull substances to earth's land, water, or air.
rock cycle: rocks changing from one form into another in a never-ending series of process.
igneous rock: a rock formed when melted rock materials cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock: a rock made of bits of matter joined together.
fossil: any remanins or printing of living things of the past.
methamorphic rock: a rock formed under heat and pressurefrom another kind of rock.
humus: decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution: adding any harmfull substances to earth's land, water, or air.
rock cycle: rocks changing from one form into another in a never-ending series of process.
Vocabulary 13 - Minerals of Earth's crust
Mineral: a solid material of Earth's crust with a definite composittion.
luster: the way ligth bounces off a mineral surface.
streak: the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed against a hard, rough surface.
hardness: how well a mineral resist scratching.
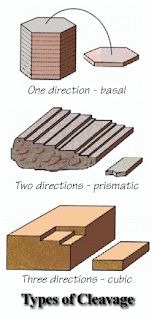
cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surface.
ore: amineral containing useful substance.
gem: a mineral valued from being rare and beautiful.
nonrenewable resource: a resource that cannot be replace within a short period of time or at all.
luster: the way ligth bounces off a mineral surface.
streak: the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed against a hard, rough surface.
hardness: how well a mineral resist scratching.
cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surface.
ore: amineral containing useful substance.
gem: a mineral valued from being rare and beautiful.
nonrenewable resource: a resource that cannot be replace within a short period of time or at all.
vocabulary 10- matter and energy
Kinetic energy: the energy of a moving object.
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.

conduction: movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a coocler object; the materials remain in place.
radiation: movement of energy in the form of waves that can that can travel through empty space.

wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electric current.
¡
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.

conduction: movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a coocler object; the materials remain in place.
radiation: movement of energy in the form of waves that can that can travel through empty space.

wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electric current.
¡
dry cell battery: a battery that uses `` dry chemicals´´ to produce an electric current.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)