desallination: getting fresh water fro seawater.
water cycle: the continious movement of water between Earth's surface and the air, hanging from liquid to gas to liquid.
groundwater: water that seeps into the ground into spaces between bits of rock and soil
water table: the top of the water-filled spaces in the ground.
aquifer: an underground of rock or soil filled with water.
spring: a place were groundwater seeps out of the ground.
well: a hole dug below the water table that water seeps into.
reservoir: a storage area for freshwater supplies.
martes, 28 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary 15- Earth's Atmosphere
renewable resource: a resource that can be replaced in a short period of time.
ozone layer: a layer of ozone gas in the atmosphere that screens out much of the sun's UV rays.
fossil fuel: a fuel formed from a decay of ancient forms of life.
smog: a mixture of smoke and fog.
acid rain: moisture that falls to Earth after being mixed with wastes fro burned fossil fuels.
ozone layer: a layer of ozone gas in the atmosphere that screens out much of the sun's UV rays.
acid rain: moisture that falls to Earth after being mixed with wastes fro burned fossil fuels.
vocabulary 14 - Earth's Rocks an Soil
rock: a naturally solid in the crust, made up of one ore more minerals.
igneous rock: a rock formed when melted rock materials cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock: a rock made of bits of matter joined together.
fossil: any remanins or printing of living things of the past.
methamorphic rock: a rock formed under heat and pressurefrom another kind of rock.
humus: decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution: adding any harmfull substances to earth's land, water, or air.
rock cycle: rocks changing from one form into another in a never-ending series of process.
igneous rock: a rock formed when melted rock materials cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock: a rock made of bits of matter joined together.
fossil: any remanins or printing of living things of the past.
methamorphic rock: a rock formed under heat and pressurefrom another kind of rock.
humus: decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution: adding any harmfull substances to earth's land, water, or air.
rock cycle: rocks changing from one form into another in a never-ending series of process.
Vocabulary 13 - Minerals of Earth's crust
Mineral: a solid material of Earth's crust with a definite composittion.
luster: the way ligth bounces off a mineral surface.
streak: the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed against a hard, rough surface.
hardness: how well a mineral resist scratching.
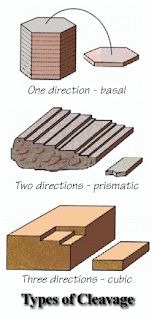
cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surface.
ore: amineral containing useful substance.
gem: a mineral valued from being rare and beautiful.
nonrenewable resource: a resource that cannot be replace within a short period of time or at all.
luster: the way ligth bounces off a mineral surface.
streak: the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed against a hard, rough surface.
hardness: how well a mineral resist scratching.
cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surface.
ore: amineral containing useful substance.
gem: a mineral valued from being rare and beautiful.
nonrenewable resource: a resource that cannot be replace within a short period of time or at all.
vocabulary 10- matter and energy
Kinetic energy: the energy of a moving object.
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.

conduction: movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a coocler object; the materials remain in place.
radiation: movement of energy in the form of waves that can that can travel through empty space.

wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electric current.
¡
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.

conduction: movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a coocler object; the materials remain in place.
radiation: movement of energy in the form of waves that can that can travel through empty space.

wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electric current.
¡
dry cell battery: a battery that uses `` dry chemicals´´ to produce an electric current.
Vocabulary 9 -Chemical Changes
Physica change: a change in size, shape, or state, without forming a new substance.
Chemical change: a change in matter that produce a new substance with different properties from the original.
Chemical reaction: a chemical change of original substance nto one or more new substances.
reactant: one of the original substance before a chemical reaction takes place.

product: one of the new substances produced when a chemical reaction takes place.
Chemical change: a change in matter that produce a new substance with different properties from the original.
Chemical reaction: a chemical change of original substance nto one or more new substances.
reactant: one of the original substance before a chemical reaction takes place.

product: one of the new substances produced when a chemical reaction takes place.
miércoles, 22 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary 8- Mixtures and Solutions
Mixture: two or more parts blended together yet kipping their own properties and not turnning into a new substance.
Solution: a mixture in wish substance are completely blended so that properties are the same throughout and the substance stay blended
suspension: a mixture of substance that separate upon standing
colloide: particles (or droplets) large enough to block out light spread throughout another substance
Emulsion: a liquid spread through another liquid
aerosol: liquid drops or solid particles spread through a gas
gel: a solid pread through a liquid
foam: a gas spread through a liquid or solid.
Solution: a mixture in wish substance are completely blended so that properties are the same throughout and the substance stay blended
suspension: a mixture of substance that separate upon standing
colloide: particles (or droplets) large enough to block out light spread throughout another substance
Emulsion: a liquid spread through another liquid
aerosol: liquid drops or solid particles spread through a gas
gel: a solid pread through a liquid
foam: a gas spread through a liquid or solid.
vocabuly 7- solid, liquids, and gases
STATE OF MATTER: ANY OF THE FORMS MATTER CAN EXIST.
MELTING POINT: THE TEMPERATURE AT WHICH A SOLID CHANGES STATE INTO A LIQUID.
BOILING POINT: THE TEMPERATURE AT WHICH A LIQUID CHANGES STAT INTO A GAS.
FREEZING POINT: THE TEMPERATURE AT WISH A LIQUID CHANGE STATE INTO A SOLID.
MELTING POINT: THE TEMPERATURE AT WHICH A SOLID CHANGES STATE INTO A LIQUID.
BOILING POINT: THE TEMPERATURE AT WHICH A LIQUID CHANGES STAT INTO A GAS.
FREEZING POINT: THE TEMPERATURE AT WISH A LIQUID CHANGE STATE INTO A SOLID.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)